Failure of lifeboat release hook
Associated links (M17A0391)
Place du Centre
200 Promenade du Portage, 4th Floor
Gatineau QC K1A 1K8
29 November 2018
General Manager
Jiangsu Jiaoyan Marine Equipment Co., Ltd.
No.22 Shuiyun Road, Yuecheng Town
Jiangyin City, Jiangsu Province
214404
China
Re :
Marine Safety Advisory MSA 04/18
Failure of lifeboat release hook
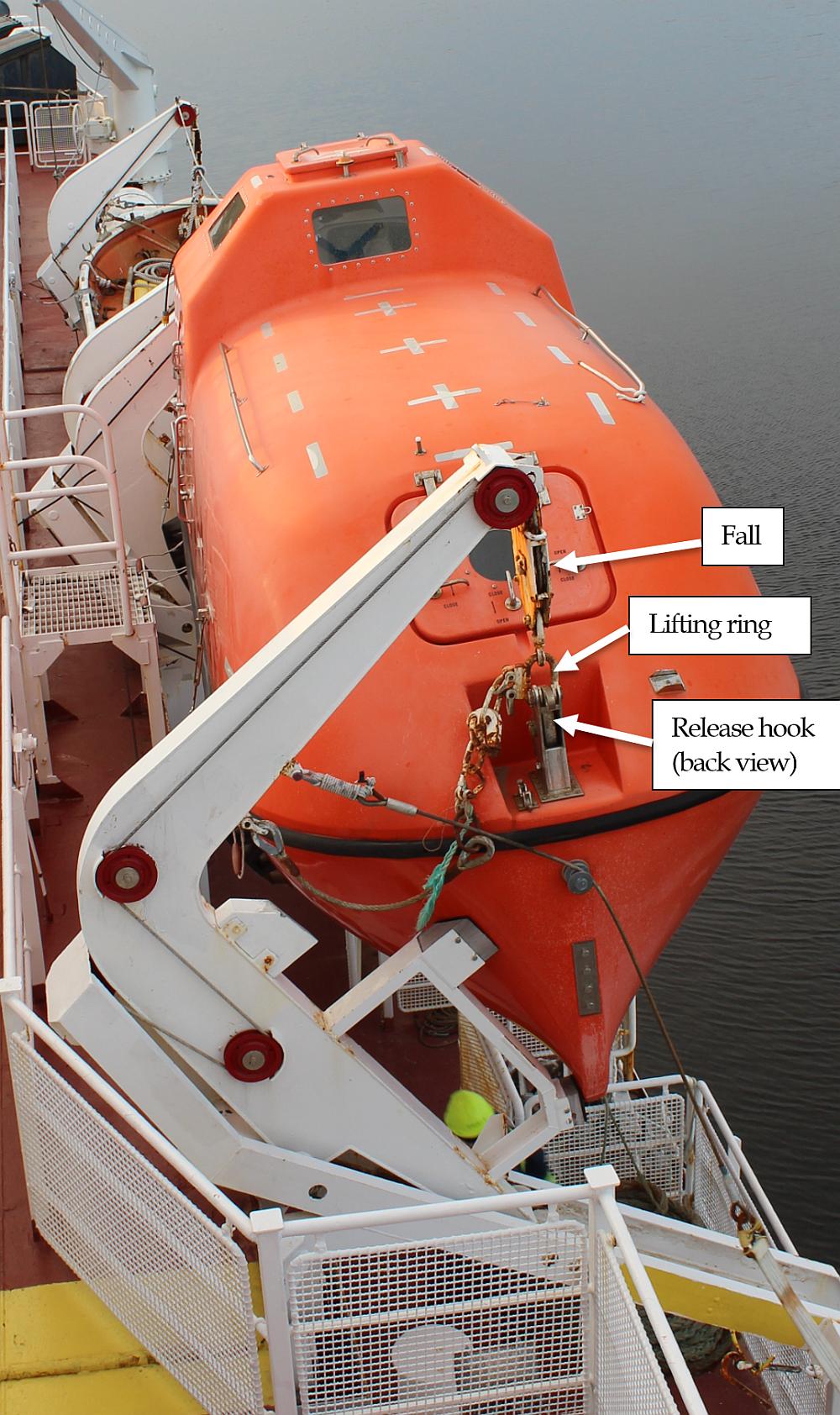
On 11 October 2017, at 1430 Atlantic Daylight Time, the passenger vessel Northern Ranger, operated by Nunatsiavut Marine (the company), experienced a failure in the starboard lifeboat’s forward release hook during a training exercise at the dock in Nain, Newfoundland and Labrador. Four crew members were on board the SOLAS-approved lifeboat (Appendix A) at the time of the occurrence.
As part of the training exercise, the lifeboat was launched, operated, and retrieved. During retrieval, the lifeboat was lifted until it was level with the embarkation deck; the forward release hook then suddenly released (Appendix B). The lifeboat swung downward, bow first, and hung from the aft release hook and fall. One crew member fell through the lifeboat’s forward hatch and into the water while 3 crew members remained inside. All 4 crew members were recovered and those who were injured were treated in hospital. The investigation M17A0391 into the occurrence is ongoing.
The lifeboat and release hooks were manufactured by Jiangsu Jiaoyan Marine Equipment Co. Ltd. in China, while the on- or off-load release mechanism was manufactured by Shanghai Shengkong Machine Company Ltd.
The TSB Engineering Laboratory tested the lifeboat’s release hook and on- or off-load release mechanism to determine the cause of the sudden hook release. The TSB Engineering Laboratory also analysed the equipment’s documentation. Testing revealed several issues with the operation of the release hook and the document analysis revealed discrepancies.
Release hook failure
As the lifeboat’s forward and aft release hooks are simultaneously reset by crew members, the on- or off-load release mechanism within the lifeboat (rigged to the release hooks with cables) is operated by a third crew member.
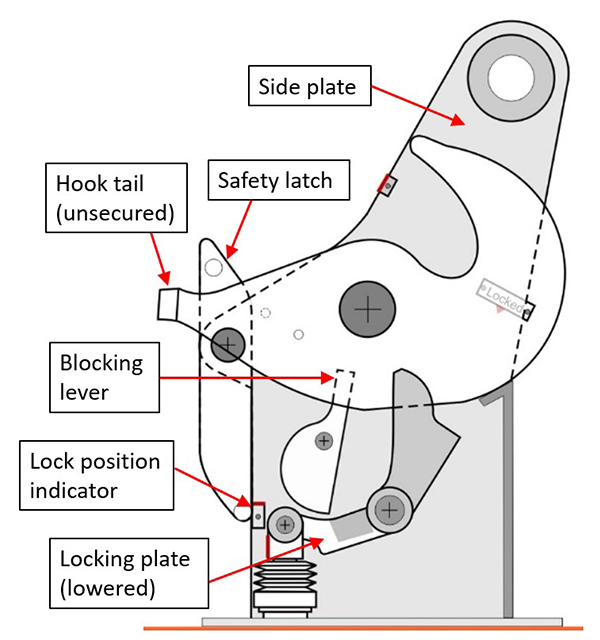
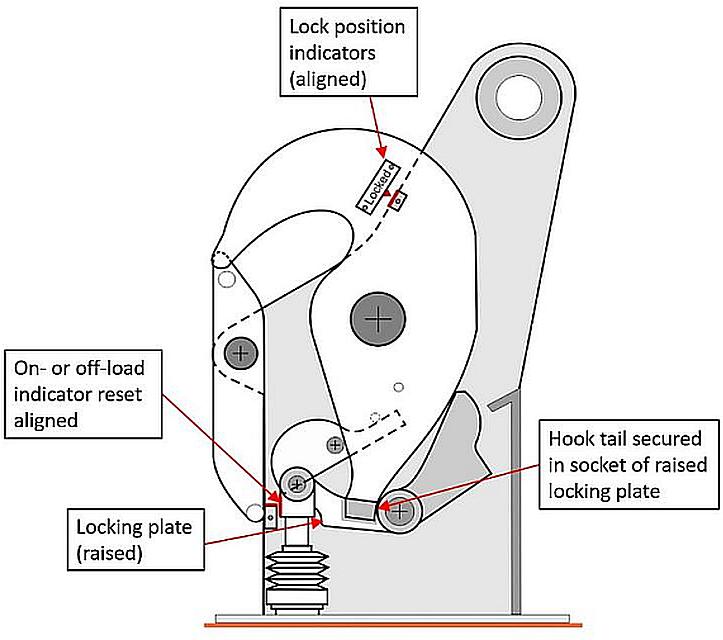
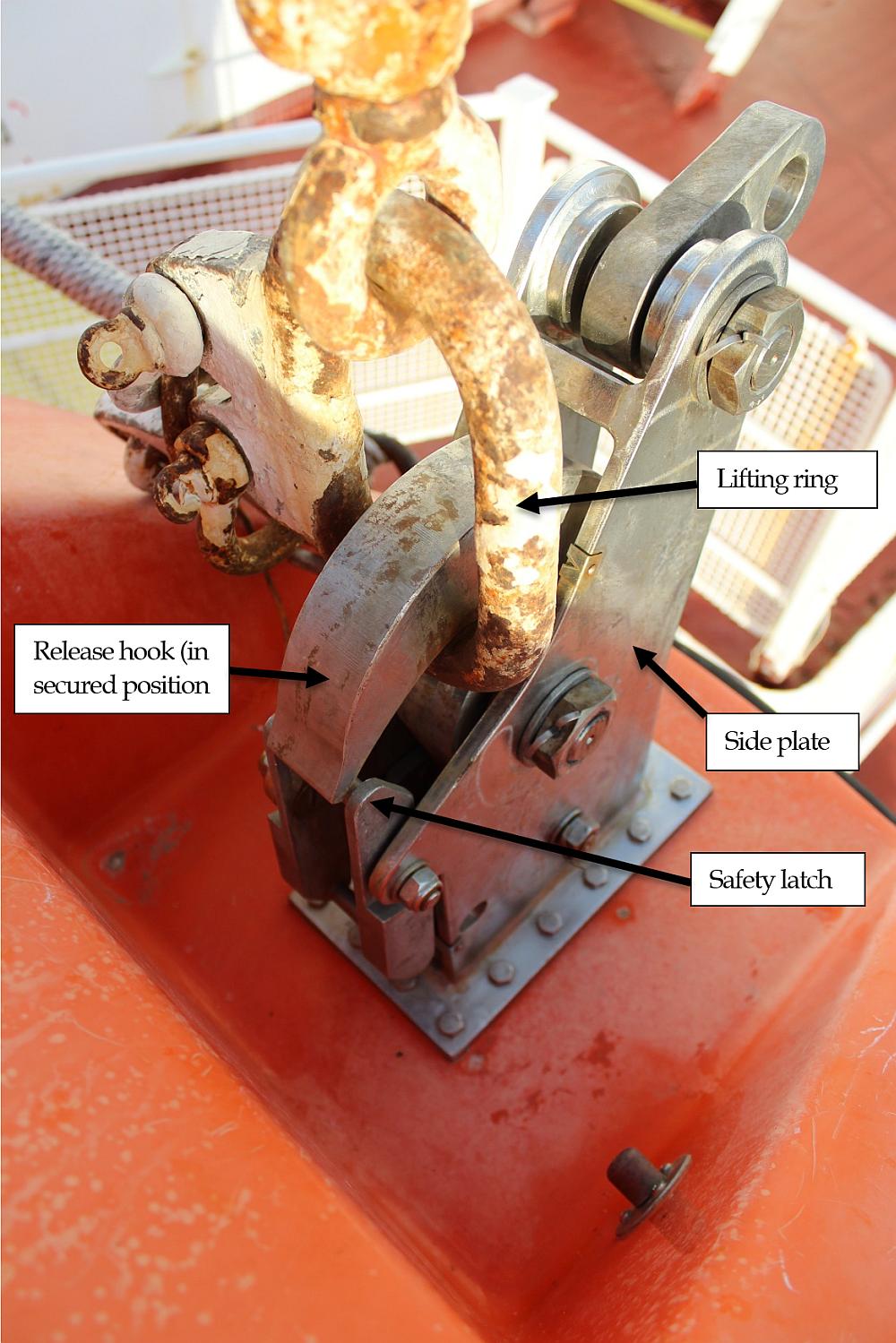
Figures 1 and 2 were created by the TSB Engineering Laboratory to show the primary components of the lifeboat release hooks used in this occurrence, and their hook/locking plate interaction. In order to be reset as designed by the manufacturer, the hooks are initially opened, allowing the blocking lever to move to a vertical position and block the locking plate from rising (Figure 1). In order to reset each release hook, each hook is rotated by a crew member, and as it rotates it interacts with its blocking lever, moving the lever out of the vertical position. The tail of each hook assumes the function of the blocking lever, blocking its locking plate from rising until the hook is rotated such that its tail is in line with the socket of its locking plate. When each tail is aligned with its locking plate socket, the locking plate is no longer blocked and is allowed to rise; the on- or off- load release mechanism can then be reset, which secures each hook in the socket of its locking plate. Once the on- or off-load release mechanism is reset, and each release hook’s reset indicators are aligned, each hook is secure and ready to receive a lifting ring, which is retained by the safety latch (Figure 2).
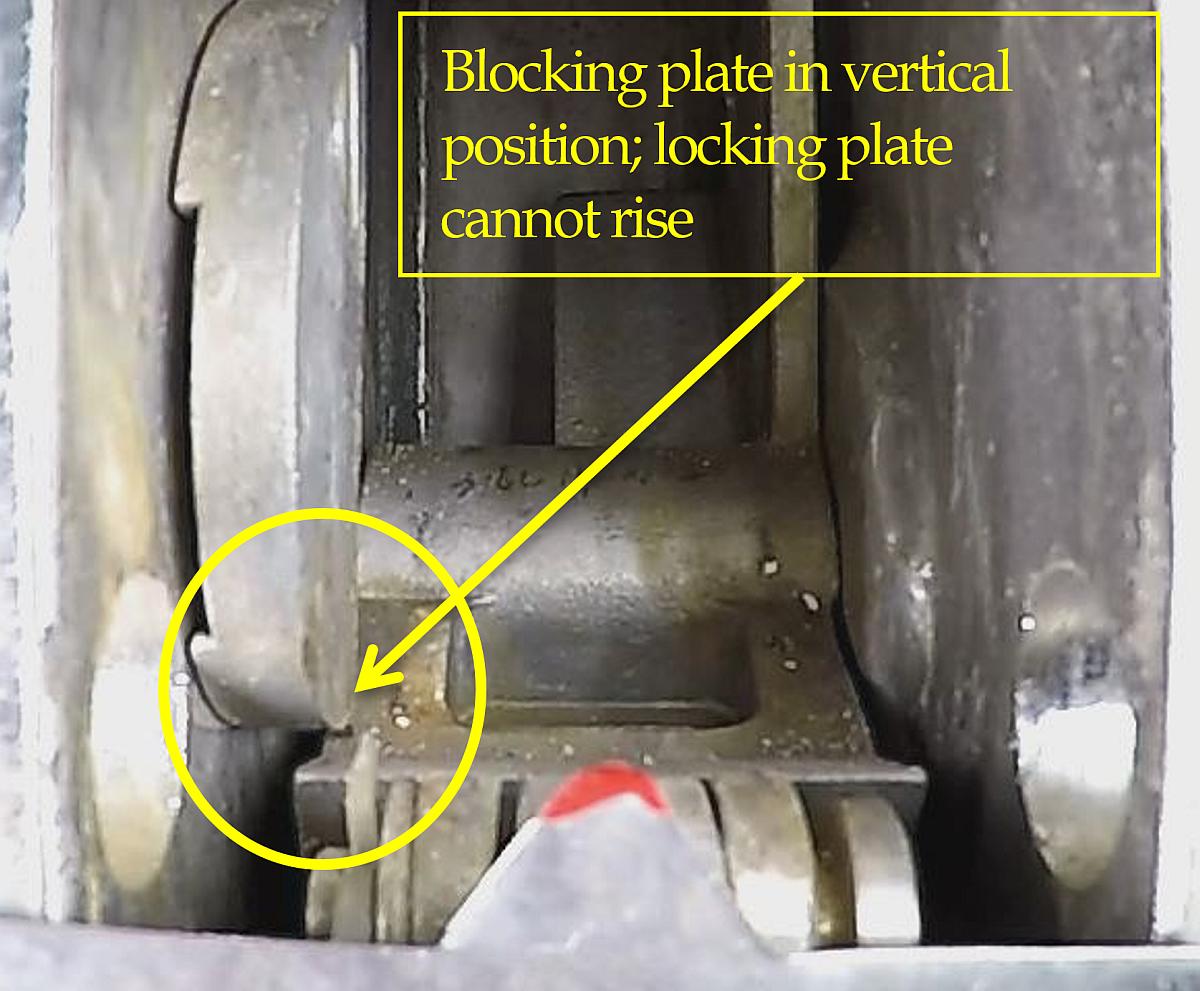
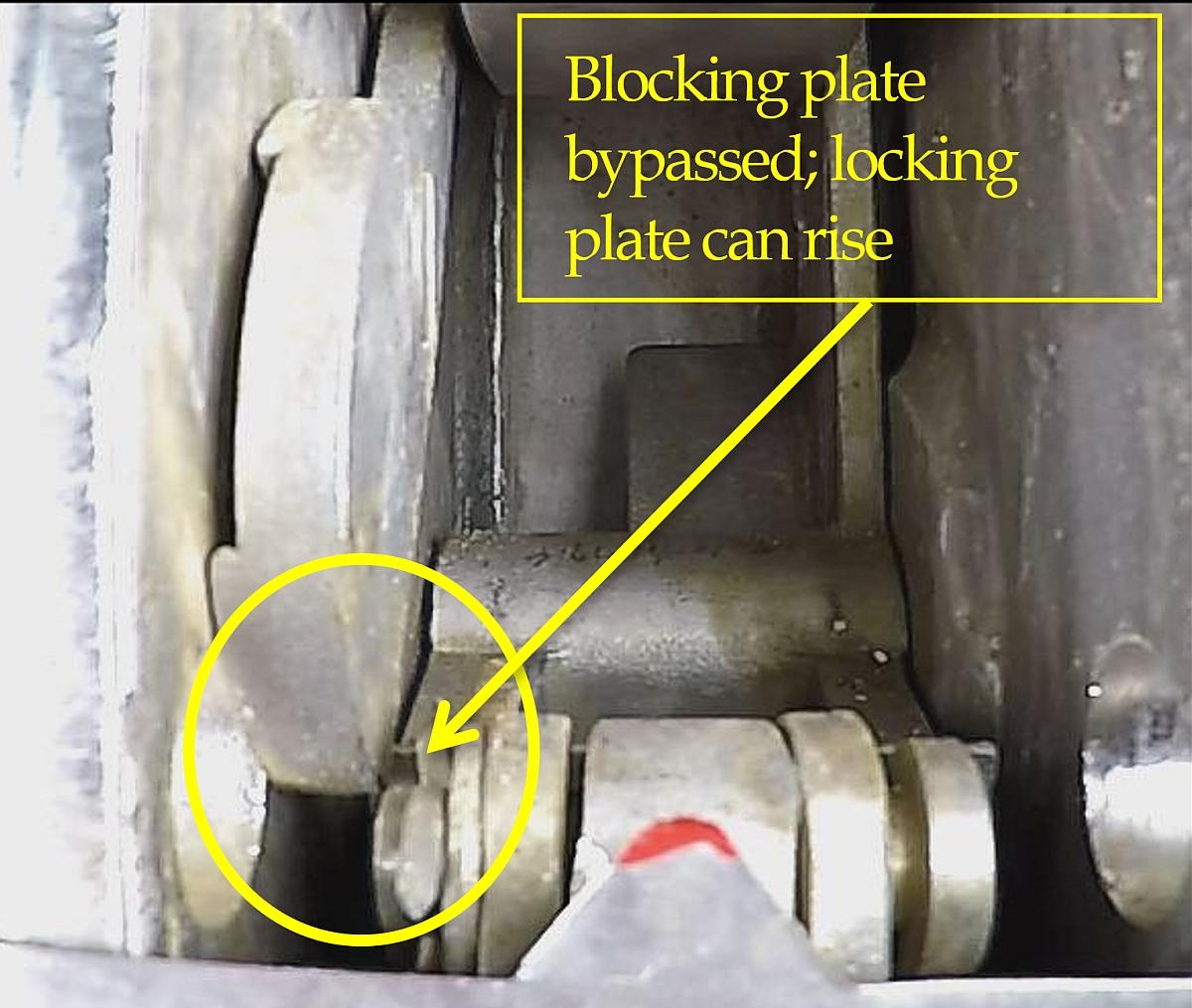
Repeated testing of the reset and locking plate operation of the release hooks was conducted to identify possible abnormalities or defects. It was observed that during the resetting procedure of either the forward or aft hook, it is possible to bypass the function of the blocking lever (Figures 3 and 4).
If the blocking lever is bypassed and the tail of each release hook is not rotated to block its locking plate from rising, the locking plate can rise. The on- or off-load release mechanism inside the lifeboat can return to its reset position without the tail of each release hook being secured in the socket of its locking plate. This can give the operator in the lifeboat the impression that the hooks are reset and secured when, in fact, they are not. Testing further identified that the blocking lever can occasionally be held back from the blocking position due to friction between the blocking lever and the side plate of the hook.
The TSB Engineering Laboratory also tested to determine if each release hook could support a load when it was reset with its tail secured in the socket of its locking plate versus not. Weight was added to the lifeboat to simulate the weight of the 4 crew members and gear on board at the time of the occurrence. The lifting rings used in the occurrence (28 mm in diameter, see Appendix B) were inserted into each reset and secured release hook, and each end of the lifeboat was lifted individually with an overhead crane. Each secured forward and aft hook supported its portion of the load without issue.
The on- or off-load release mechanism was then intentionally reset without the tail of each hook secured in its locking plate. The 28 mm lifting rings used in the occurrence were inserted in each release hook, and each end of the lifeboat was lifted individually by the crane. When unsecured, each forward and aft release hook supported its portion of the load.
Next, the TSB Engineering Laboratory tested for accidental release of the unsecured hooks. While each 28 mm lifting ring was supporting its portion of the load, it was struck several times with a rubber mallet to simulate the shock or vibrations between the fall and the davit arm during retrieval of the lifeboat. On the first test, each unsecured release hook opened with 1 strike. On the second and third test, each hook would not open with repeated strikes. Testing determined that the unsecured release hooks would initially hold their respective portions of the overall load but would sometimes open when struck, other times not.
Overall, testing determined that the release hooks on the Northern Ranger lifeboat were capable of supporting the load of the lifeboat even when the hooks were not secured. However, the on- or off-load release mechanism would appear to be reset, giving the operator in the lifeboat the impression that the release hooks were secured. As a result, a lifeboat with this hook assembly can experience a sudden release during retrieval, as in this occurrence. The deficiencies identified by the TSB Engineering Laboratory’s testing may be present in other release hooks produced by the manufacturer, putting other vessels and crew at risk.
Issues with size of lifting ring and documentation
Lifting ring absent from manufacturer’s final drawing
The lifeboat manufacturer’s final drawing of its release hook and on- or off-load release mechanism provided to the Northern Ranger and to the lifeboat’s classification society do not depict a lifting ring.
A lifting ring is shown on a drawing included in the strength calculations for the release hook; these strength calculations were submitted by the manufacturer to the lifeboat’s classification society for approval. Neither the company nor the crew on board the Northern Ranger had access to the strength calculations document. The diameter of the lifting ring shown in the drawing is not apparent; the TSB had to analyze the strength calculations document (reviewed measurements and formulas, performed mathematical calculations) to determine that the diameter of the lifting ring depicted is 45 mm.
During testing, the TSB Engineering Laboratory reset and secured the release hooks as per the manufacturer’s operating instructions, which indicate that the release hook should be reset and secured before a lifting ring is inserted. Using the depicted 45 mm diameter lifting ring, the TSB identified that when the release hook is secured in the reset position, the hook opening is not large enough to insert a 45 mm lifting ring.
In order to use a 45 mm lifting ring as the manufacturer’s strength calculations imply, operators have to modify the operating instructions and insert each lifting ring into its hook as the hook and on- or off-load release mechanism are being reset, rather than after the hook is already secured in the reset position.
Testing revealed that if a 45 mm lifting ring is used, the hooks will operate as designed and not support a load when the hooks are not secured.
Operator’s manual sent to company and classification society
The operator’s manual was provided to the company by the manufacturer, and was on board the Northern Ranger at the time of the occurrence.
The operator’s manual contains a graphic of the release hook with a lifting ring of an unspecified diameter inserted in it, and includes operating instructions for the launching and retrieval of the lifeboat. Testing at the TSB Engineering Laboratory determined that, if followed, the operating instructions allow operators to reset the lifeboat’s release hooks and on- or off-load release mechanism, and insert the 28 mm diameter lifting rings that were on board the Northern Ranger at the time of the occurrence.
The 28 mm diameter lifting rings used in this occurrence allowed the release hooks to support a load with the lifeboat’s on- or off-load release mechanism reset and hooks unsecured. This may not meet the requirements of section 4.4.7.6.8 of The International Lifesaving Appliance (LSA) Code (2011), which indicates that release hooks should not support a load in the unsecured position.
Without documentation that clearly indicates a lifting ring of a specified diameter, operators may use a lifting ring that will allow the release hook to operate in a manner that does not meet its classification society’s approval and, by extension, LSA Code and SOLAS requirements.
This information is provided for whatever follow-up action is deemed appropriate. The TSB would appreciate being advised of any action that is taken in this regard.
Upon completion of investigation M17A0391 the Board will release its investigation report into this occurrence.
Original signed by
Marc-André Poisson
Director, Marine
Transportation Safety Board of Canada
cc:
- Canadian Representative
Rina Classification Society - HSE Superintendent/DPA
Nunatsiavut Marine - Arctic & Large Vessels, Design and Equipment Standards
Transport Canada Safety and Security - IACS Membership